Since the growth in operating liabilities is outpacing the growth in operating assets, we’d reasonably expect the change in NWC to be positive. In the absence of further contextual details, negative net working capital (NWC) is not necessarily a concerning sign about the financial health of a company. In fact, cash and cash equivalents are more related to investing activities, because the company could benefit from interest income, while debt and debt-like instruments would fall into financing activities. However, as we’ll see shortly, some businesses have ways of getting suppliers and customers to lend beyond the level of Current Asset funding needs. This dynamic arises when operating lenders (e.g., inventory suppliers, landlords, and customers) provide funding greater than what is required to fund items like Accounts Receivable and Inventory. However, having significant businesses with too much working capital does not necessarily always indicate better financial performance.
What is the difference between positive and negative working capital?
The benefit of neglecting inventory and other non-current assets is that liquidating inventory may not be simple or desirable, so the quick ratio ignores those as a source of short-term liquidity. The quick ratio—or “acid test ratio”—is a closely related metric that isolates only the most liquid assets, such as cash and receivables, to gauge liquidity risk. Working capital is a core component of effective AI in Accounting financial management, which is directly tied to a company’s operational efficiency and long-term viability.
Accounts Payable Essentials: From Invoice Processing to Payment
When a business’s current assets are exactly equal to its current liabilities, then it is called a zero working capital situation. This happens when a company’s current liabilities completely fund its current assets. Zero working capital can increase the effectiveness of a business’s investment. Negative working capital becomes a bad sign when a business is unable to meet its operational expenses or settle its short-term financial obligations.
Q: Do e-commerce companies have a negative working capital?

Grocery stores operate on thin profit margins and often have negative working capital. They typically pay their suppliers on a weekly or bi-weekly basis, while customers pay for their groceries immediately. This means that grocery stores can use the cash they receive from customers to cover their expenses until they have to pay their suppliers.

Negative working capital definition
The net working capital (NWC) metric is different from the traditional working capital metric because non-operating current assets and current liabilities are excluded from the calculation. The formula to calculate the working capital ratio divides a company’s current assets by its current liabilities. In financial accounting, working capital is a specific subset of balance sheet items and is calculated by subtracting current liabilities from current assets. Shortening your accounts payable period can have the opposite effect, so business owners will want to carefully manage this policy. Ultimately, understanding net working capital provides insights into how effectively businesses are managing their recurring operational costs. Therefore, by considering net working capital during their evaluations, analysts and investors get a clear picture of a company’s operational efficiency, financial strength and, hence, its overall value.
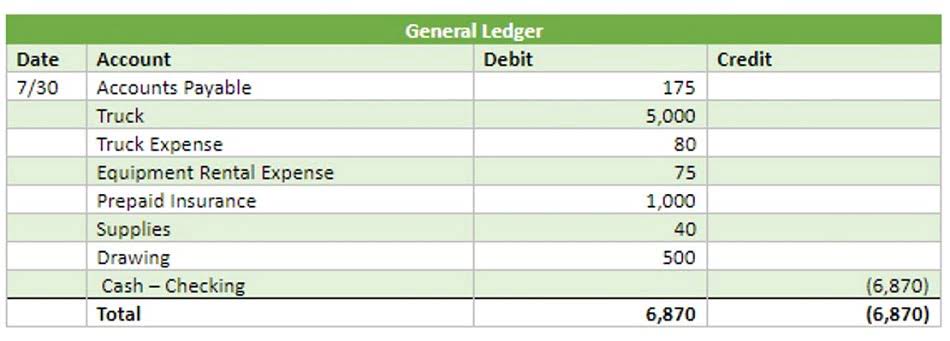
As a business owner, have you ever spent cash from sales before paying your suppliers? Negative working capital can have manifold consequences for businesses that don’t generate large amounts of cash flow from inventory turnover. Negative working capital occurs when a business decides to spend more cash from revenue before settling short-term obligations and supplier payments. It means their current liabilities will be greater than their current assets. The problem arises when businesses lack reserves to meet their operational expenses. Net working capital (NWC) measures a company’s liquidity and ability to handle short-term financial obligations.

HighRadius gross vs net is redefining treasury with AI-driven tools like LiveCube for predictive forecasting and no-code scenario building. Its Cash Management module automates bank integration, global visibility, cash positioning, target balances, and reconciliation—streamlining end-to-end treasury operations. Negative working capital can limit opportunities to expand or fund growth innovations.
- This formula essentially captures a Business’ investment in short-term Operating Assets and the degree to which the Assets cover the short-term obligations of the Business.
- Changes in working capital are often used by investors and lenders to assess the health and value of a business.
- For example, imagine the appliance retailer ordered too much inventory – its cash will be tied up and unavailable for spending on other things (such as fixed assets and salaries).
- • Some companies use negative working capital strategically to free up cash by delaying payments to suppliers.
- For instance, net working capital is an integral component of the Free Cash Flow to Firm (FCFF) and Free Cash Flow to Equity (FCFE) models, enabling a more thorough analysis of a company’s financial health.
This may seem like a bad thing, but it can actually be a sign of financial efficiency. In this section, we will explore how negative working capital can be incorporated into financial modeling, including DCF, LBO, and comps. Working capital can be negative if a company’s current assets are less than its current liabilities. Working capital is negative nwc calculated as the difference between a company’s current assets and current liabilities.
